NIS 2 Compliance Made Simple
Streamline your NIS 2 compliance process with Drata’s ready-to-use policies, continuous control monitoring & automated evidence collection.
Streamline your NIS 2 compliance process with Drata’s ready-to-use policies, continuous control monitoring & automated evidence collection.
Streamline Your Path to NIS 2 Compliance and Beyond

Excellent Based on 1000+ Reviews
Meet Drata
We’ve Got You Covered in All Things NIS Compliance
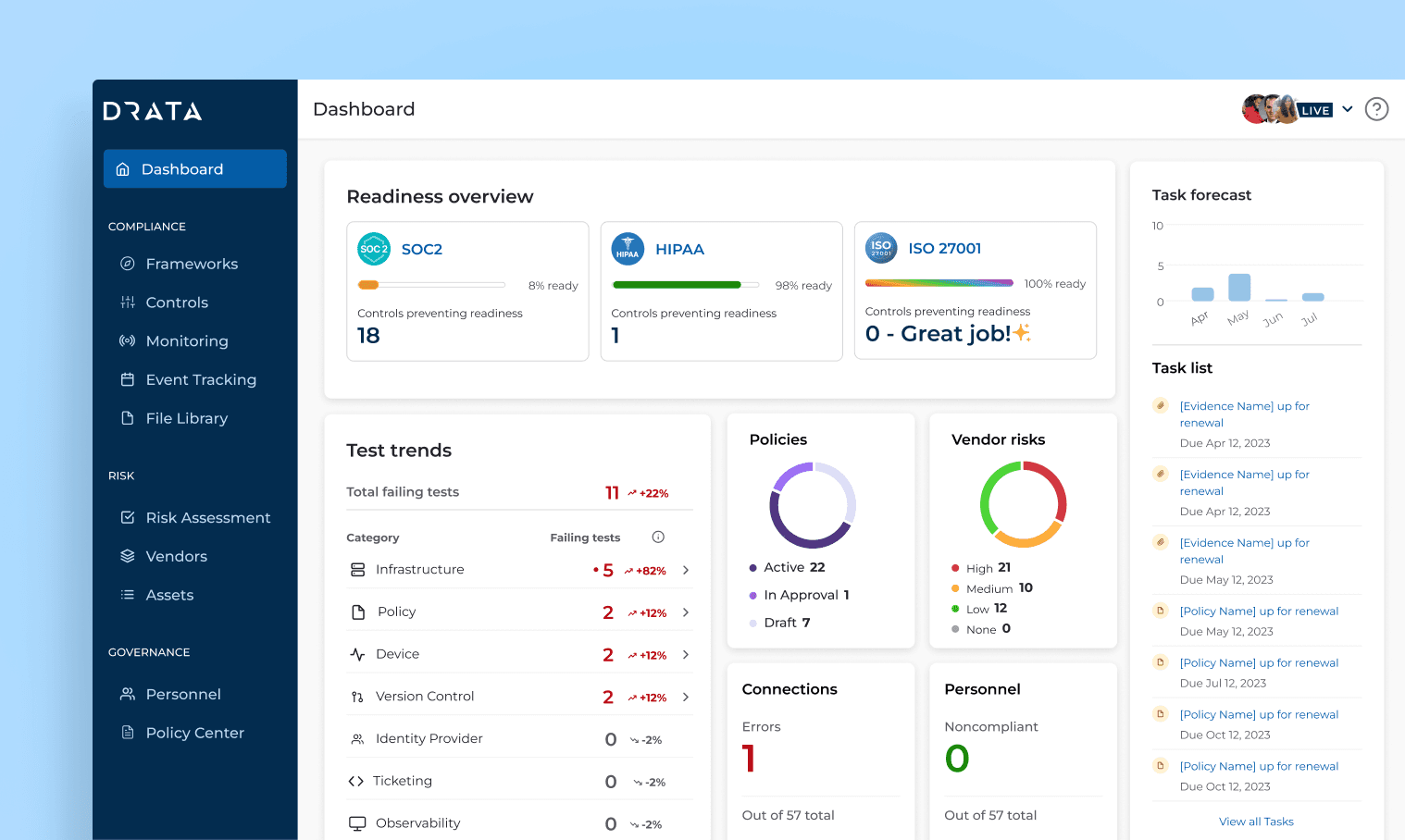
Not a compliance expert? Not a problem. Make the entire audit process a breeze with step-by-step guides and Drata’s intuitive platform that ranks highest for ease of use on G2.
By constantly adding new frameworks and features, we keep you ahead of regulatory changes and emerging threats, ensuring your risk management status remains proactive.

Drata automatically collects evidence, so you can say goodbye to screenshots and spreadsheets.

Feed your Trust Center documents from Drata, workflows and analytics from your CRM, and work faster with connected productivity apps

Streamline documentation, employee acceptance, and version history with 20+ editable, auditor-approved policies.

Drata’s built-in self-assessments enable you to efficiently report on your security program’s effectiveness.

Choose from Drata's controls or create custom controls to meet your specific needs and framework requirements.

Drata’s support team consists of compliance experts and former auditors. Our experts are a click away.
Customers
Don’t Take Our Word for It
See why companies like you love using Drata.
Resources
Looking for more?
Discover the latest compliance resources and jumpstart your GRC program today.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is NIS regulation?
The NIS regulation, known as the Network and Information Security Directive (now updated to NIS 2), is an EU directive aimed at improving cybersecurity across member states. It sets obligations for entities within specific critical sectors to adopt cybersecurity measures, risk management practices, and incident reporting protocols to protect network and information systems from cyber threats.
What are the NIS requirements?
NIS 2 emphasizes three key pillars for compliance:
Comprehensive Cybersecurity Risk Management: Organizations must take proactive steps to establish strong information security policies that cover incident prevention, detection, response, business continuity, crisis management, and supply chain security.
Incident Reporting and Supervision: Entities must report incidents without undue delay. This includes early warnings, incident notifications within 72 hours, and a final report within a month after incident notification.
Enforcement and Management Liability: Management bodies of affected entities are responsible for cybersecurity measures and may face penalties for non-compliance, including significant fines of up to €10 million or 2% of worldwide annual turnover.
Although NIS2 is an EU directive, does it still apply to American businesses like GDPR does?
Yes, NIS2 can apply to American businesses if they offer services or have operations in the EU and fall under the categories of essential or important entities defined by the directive. Similar to the GDPR, NIS2 has extraterritorial reach, meaning non-EU businesses must comply if they meet the criteria and provide services within the EU.
What are the NIS requirements?
Organizations need to comply by October 2024 when the NIS 2 Directive is to be transposed into national law.
What are the consequences for not implementing NIS2?
Under the NIS2 Directive, organizations that fail to comply can face administrative fines of up to €10 million or 2% of their total worldwide annual turnover, whichever is higher. Additional penalties may include temporary bans on managerial duties or mandatory corrective actions.
What is the difference between NIS and NIST?
NIS is a European Union directive focusing on cybersecurity standards across member states to protect critical infrastructure and network information systems. NIST, on the other hand, stands for the National Institute of Standards and Technology, a U.S.-based organization that develops standards, guidelines, and best practices, including the widely adopted NIST Cybersecurity Framework. While NIS is legally binding for entities in the EU, NIST provides voluntary guidance used globally.